PO 7. Recognize the role of the following in supplying nutrients from the soil.
- Soil solution
- Cation exchange sites
- Soil organic matter
- Soil minerals
- Plant residue
|
|
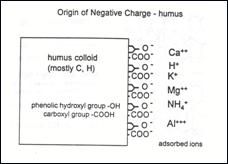
The soil solution is the liquid in the soil. Plant nutrients (solids and gases) dissolved in the soil solution can move into the plant as the water is taken up by the roots. This is the medium through which most nutrients are taken up by the plant. Cations are positively-charged ions (such as Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, and NH4+) which are held on anionic (negatively-charged) exchange sites in the soil. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) is a measure of the amount of cations that can be held by the soil and released into the soil solution. Soils with a greater cation exchange capacity are able to hold onto more nutrients. See PO 10 for more information. Soil organic matter refers to hydrocarbon compounds in various stages of decomposition. Humus is organic material resistant to further decomposition, and which does not supply many nutrients. It can cause a negative charge in the soil, increasing CEC. |