Competency Area 3: Soil Testing and Plant Tissue Analysis
PO 23. Recognize how the following terms relate to plant nutrient level.
- Critical value or range.
- Sufficiency range.
- Optimum, below optimum, and above optimum soil nutrient levels.
- Luxury consumption.
- Toxicity level.
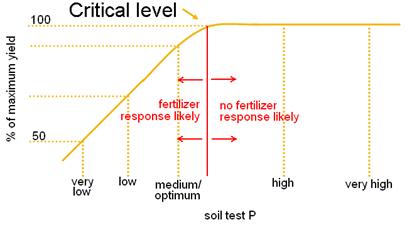
Critical value or range indicates the soil or tissue content below which the plant most likely is deficient in that specific nutrient and production could be enhanced by addition of the nutrient. Below that critical value, the nutrient levels are below optimum. The sufficiency range is the nutrient level at which the plant has enough nutrients to function and develop properly, but not so much that it is poisoned. This is reported as "medium" or "high" on soil tests. Optimum, below optimum, and above optimum soil nutrient levels are terms used to describe whether plants have sufficient nutrients. If soil test levels are below the critical agronomic value, the test will come back as below optimum; if soil test levels are above the critical agronomic value, the test will come back as above optimum. |
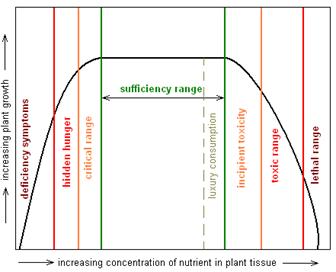 |
Luxury consumption occurs when soil nutrient levels are above optimum and plants take up more of a nutrient than needed for functioning and production. Potassium (K) is commonly taken up in excess.
The toxicity level is the nutrient level at which there is so much of a nutrient that it can harm the plants. This value will be reported as either a "high" or "very high" level on a soil test.

Corn plants exhibiting symptoms of low (left), adequate (middle), and excessive (right) nitrogen.
Quick Links
- Competency Area 1: Basic Concepts of Plant Nutrition
- Competency Area 2: Basic Concepts of Soil Fertility
- Competency Area 3: Soil Testing and Plant Tissue Analysis
- Competency Area 4: Nutrient Sources, Analyses, Application Methods
- Competency Area 5: Soil pH and Liming
- Competency Area 6: Nutrient Management and Planning
